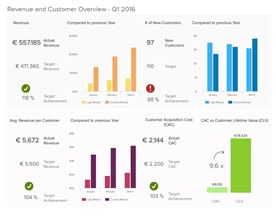
What are the key metrics for business success via return on sales? Key ROS metrics: Profit Margin, Operating Efficiency, Cost Management. Master these to drive business success through improved financial health.
Return on sales (ROS) is a financial metric that is used to assess a company’s profitability. It is also referred to as operating profit margin and is expressed as a percentage of revenue. ROS is a critical measure for businesses of all sizes and industries because it provides insight into how efficiently a company is using its resources to generate profits.

Understanding Return on Sales
ROS is a profitability ratio that measures the amount of profit generated by a company for every dollar of sales. It is calculated by dividing the company’s operating income by its net sales. ROS is a useful metric because it allows businesses to compare their profitability to other companies in the same industry.
Calculating Return on Sales
Calculating ROS is a straightforward process that involves dividing a company’s operating income by its net sales. Operating income is the amount of profit a company generates after deducting its operating expenses from its revenue. Net sales are the total amount of revenue generated by a company after deducting any returns or discounts.
Key Takeaways
- ROS is a profitability ratio that measures the amount of profit generated by a company for every dollar of sales.
- Calculating ROS involves dividing a company’s operating income by its net sales.
- ROS is a critical measure for businesses of all sizes and industries because it provides insight into how efficiently a company is using its resources to generate profits.
Understanding Return on Sales
Definition of Return on Sales
Return on Sales (ROS), also known as profit margin, is a financial ratio that measures the efficiency of a company in generating profit from its sales revenue. It is calculated by dividing the net profit by the total revenue generated by the company during a particular period. ROS is expressed as a percentage and indicates the amount of profit that a company earns for every dollar of sales.
ROS is a critical metric for businesses as it helps to evaluate their profitability and efficiency. A high ROS indicates that a company is generating more profit from its sales, while a low ROS indicates that a company is struggling to generate profit from its sales revenue.
Importance of ROS in Business
ROS is an essential metric for businesses as it helps to determine the overall health of a company. It provides insights into a company’s ability to generate profit from its sales, which is crucial for its long-term sustainability. A high ROS indicates that a company is operating efficiently and generating more profit from its sales revenue, while a low ROS indicates that a company needs to improve its operations to increase profitability.
ROS is also a useful metric for investors as it helps them to evaluate the performance of a company. A high ROS indicates that a company is profitable and has the potential to provide good returns to its investors, while a low ROS indicates that a company is struggling to generate profit and may not be a good investment option.
In conclusion, ROS is a critical metric for businesses and investors as it helps to evaluate the profitability and efficiency of a company. By monitoring ROS, companies can identify areas for improvement and make strategic decisions to increase profitability.
For more information on ROS and its importance in business, refer to this source.
Calculating Return on Sales
Return on sales (ROS) is a financial metric that measures a company’s profitability by calculating the percentage of operating profit generated from net sales. It is a useful tool for investors, analysts, and managers to evaluate a company’s financial health and performance. In this section, we will discuss the return on sales formula and the step-by-step calculation process.
Return on Sales Formula
The return on sales formula is simple and straightforward. It is calculated by dividing the operating profit by net sales and multiplying the result by 100 to get the percentage.
Return on Sales Ratio = (Operating Profit / Net Sales) x 100
Step-by-Step Calculation Process
To calculate the return on sales ratio, you need to follow these steps:
- Determine the operating profit: Operating profit is the profit generated from a company’s core operations after deducting the operating expenses. It is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and depreciation from net sales.
- Calculate the net sales: Net sales are the total revenue generated from the sales of goods or services after deducting any discounts, returns, and allowances.
- Divide the operating profit by net sales: Divide the operating profit by net sales to get the return on sales ratio.
- Multiply the result by 100: Multiply the result by 100 to get the percentage.
It is important to note that the return on sales ratio varies by industry and company size. A high return on sales ratio indicates that a company is generating a significant profit from its sales, while a low ratio suggests that the company is struggling to generate profits from its operations.
To learn more about return on sales and how it is used in financial analysis, check out this resource from Investopedia, a trusted source for financial education and information.
Interpreting ROS Values
Return on Sales (ROS) is a financial ratio that measures a company’s operating margin as a percentage of revenue. It is a key metric that helps investors and analysts evaluate a company’s profitability. A high ROS indicates that a company is generating more profit from each dollar of sales, while a low ROS suggests that a company’s operating costs are eating into its revenue.
What Constitutes a Good ROS
The definition of a good ROS varies by industry. Generally, a ROS of 10% or higher is considered good, but some industries, such as technology and healthcare, may have higher benchmarks. It is important to note that a high ROS does not necessarily mean that a company is performing well. A company may have a high ROS but still have low revenue or face other financial challenges.
Industry Benchmarks and Comparisons
To understand a company’s ROS, it is important to compare it to industry benchmarks and competitors. Industry benchmarks can provide a baseline for evaluating a company’s performance and help identify areas for improvement. Comparing a company’s ROS to its competitors can also provide valuable insights into its relative performance.
One useful resource for industry benchmarks is the Financial Ratios Benchmarks database from BizMiner. This database provides industry-specific financial ratios based on data from over 5,000 industries. It can be a valuable tool for investors and analysts looking to evaluate a company’s financial performance.
In conclusion, interpreting ROS values requires an understanding of industry benchmarks and comparisons. A good ROS varies by industry, and investors should compare a company’s ROS to its competitors to gain valuable insights into its financial performance.
Factors Affecting Return on Sales
Return on sales (ROS) is a financial metric that measures the amount of profit a company generates for each dollar of sales revenue. ROS is an important metric for businesses because it indicates how efficiently a company is using its resources to generate profits. However, there are several factors that can affect a company’s ROS.
Operating Expenses Impact
Operating expenses are the costs that a company incurs to keep the business running. These expenses can include salaries, rent, utilities, marketing, and other costs. Operating expenses can have a significant impact on a company’s ROS. If a company’s operating expenses are too high, it can reduce the amount of profit generated from each dollar of sales revenue. Therefore, it is important for companies to manage their operating expenses carefully to maximize their ROS.
Revenue Streams and Sales Volume
The amount of revenue a company generates and the volume of sales can also impact ROS. If a company has multiple revenue streams, it can help to diversify the company’s income and reduce risk. However, if a company relies too heavily on one revenue stream, it can be vulnerable to changes in the market. Similarly, if a company has a high volume of sales, it can help to increase profits. However, if a company’s sales volume is too low, it can reduce the amount of profit generated from each sale.
Cost of Goods Sold and Gross Profit
The cost of goods sold (COGS) is the cost a company incurs to produce the goods or services it sells. Gross profit is the amount of revenue a company generates minus the cost of goods sold. COGS and gross profit can have a significant impact on a company’s ROS. If a company’s COGS is too high, it can reduce the amount of gross profit generated from each sale. Therefore, it is important for companies to manage their COGS carefully to maximize their ROS.
In conclusion, ROS is an important metric for businesses to monitor, as it indicates how efficiently a company is using its resources to generate profits. However, there are several factors that can impact a company’s ROS, including operating expenses, revenue streams and sales volume, and cost of goods sold and gross profit. Therefore, it is important for companies to carefully manage these factors to maximize their ROS. For more information on ROS, please refer to this link.
Return on Sales and Profitability
Link Between ROS and Profitability
Return on sales (ROS) is a profitability ratio that measures a company’s ability to generate profits from its sales revenue. It is calculated by dividing the net income by the total revenue. ROS is a key financial ratio that provides insights into how efficiently a company is using its resources to generate profits. A high ROS indicates that a company is generating a healthy profit margin from its sales revenue.
ROS is closely related to a company’s operating profit margin. Operating profit margin measures the percentage of revenue that remains after deducting all operating expenses. A high operating profit margin indicates that a company is generating a healthy profit margin from its operations. ROS and operating profit margin are both important measures of profitability and should be used together to evaluate a company’s financial performance.
ROS vs. Other Profitability Ratios
ROS is just one of many profitability ratios that can be used to evaluate a company’s financial performance. Other commonly used profitability ratios include gross profit margin and earnings per share. Gross profit margin measures the percentage of revenue that remains after deducting the cost of goods sold. Earnings per share measures the amount of profit that is allocated to each outstanding share of common stock.
While all of these ratios are important, ROS is particularly useful because it provides a clear picture of how efficiently a company is generating profits from its sales revenue. By focusing on ROS, investors can gain a better understanding of a company’s financial health and make more informed investment decisions.
To learn more about ROS and other profitability ratios, check out this resource from Investopedia, a trusted source for financial information.
Strategic Uses of ROS
Return on sales (ROS) is a crucial financial metric that measures the profitability of a company. It is calculated by dividing the net income by the total revenue. ROS provides valuable insights into a company’s financial health, operational efficiency, and business profit. In this section, we will discuss the strategic uses of ROS and how it can be used to benefit different stakeholders.
Performance Measurement and Goals
ROS is an essential tool for measuring a company’s performance and setting goals. It helps companies to identify areas where they need to improve and make necessary changes to achieve their desired level of profitability. By setting ROS targets, companies can track their progress and make informed decisions about their business operations.
For example, if a company has an ROS of 10%, it can set a goal of increasing it to 15% within the next two years. This goal can be achieved by increasing revenue, reducing expenses, or a combination of both. By monitoring ROS regularly, companies can ensure that they are on track to achieve their goals.
Investor and Creditor Analysis
ROS is an important metric for investors and creditors. It provides them with valuable insights into a company’s financial health and profitability. Investors use ROS to evaluate a company’s potential for growth and to determine whether it is a good investment opportunity.
Creditors, on the other hand, use ROS to assess a company’s ability to repay its debts. A high ROS indicates that a company has a healthy financial position and is capable of meeting its financial obligations.
In addition, ROS can also be used to compare companies within the same industry. Investors and creditors can use ROS to identify companies that are performing better than their competitors and make informed investment decisions.
Overall, ROS is a valuable metric that can be used for a variety of strategic purposes. By using ROS to measure performance and set goals, companies can improve their profitability and operational efficiency. Investors and creditors can use ROS to evaluate a company’s financial health and potential for growth.
Return on Sales in Financial Statements
Return on Sales (ROS) is a financial metric that measures a company’s profitability by calculating the percentage of sales revenue that is converted into operating profit. ROS is an important metric as it helps investors and analysts evaluate a company’s ability to generate profits from its sales revenue.
Locating ROS Information
ROS information can be found in a company’s income statement. The income statement is a financial statement that shows a company’s revenues, expenses, and profits over a specific period. The ROS formula is calculated by dividing operating profit by net sales revenue.
To locate ROS information in the income statement, investors and analysts should look for the line item labeled “Operating Profit” or “Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT).” They should then locate the line item labeled “Net Sales Revenue” and use the ROS formula to calculate the percentage.
Income Statement Analysis
ROS is an important metric for investors and analysts as it provides insight into a company’s profitability. A high ROS indicates that a company is efficiently converting its sales revenue into profits, while a low ROS may indicate that a company is struggling to generate profits from its sales.
Investors and analysts can use ROS to compare a company’s profitability to its competitors. They can also use ROS to track a company’s profitability over time and identify trends.
In conclusion, ROS is an essential financial metric that investors and analysts should use to evaluate a company’s profitability. By locating ROS information in the income statement and analyzing it, investors and analysts can gain valuable insights into a company’s financial health.
Here is a helpful resource to learn more about ROS.
Limitations and Considerations

Potential Misinterpretations
Return on sales (ROS) is a widely used financial metric that measures a company’s profitability by expressing its net income as a percentage of its revenue. However, there are several limitations and considerations to keep in mind when interpreting ROS.
One potential misinterpretation of ROS is that it does not provide information about a company’s cash flow, which is an important metric for assessing a company’s liquidity and solvency. ROS only measures profitability based on accounting principles, which may not reflect the actual cash flow of a company.
Another potential misinterpretation is that ROS does not account for trends in a company’s revenue or expenses. ROS only provides a snapshot of a company’s profitability at a given point in time, and may not reflect long-term trends or changes in a company’s market or industry.
Beyond ROS: Comprehensive Financial Analysis
While ROS is a useful metric for assessing a company’s profitability, it should not be used in isolation. A comprehensive financial analysis should also consider other financial metrics, such as efficiency ratios and cash flow analysis, to provide a more complete picture of a company’s financial health.
Efficiency ratios, such as inventory turnover and accounts receivable turnover, can provide insight into a company’s operational efficiency and effectiveness. Cash flow analysis can provide information about a company’s ability to generate cash and meet its financial obligations.
It is important to keep in mind that financial metrics should be used in conjunction with other qualitative and quantitative information, such as market trends and competitive analysis, to make informed business decisions.
External Resource
For more information about financial metrics and analysis, refer to the Financial Analysis and Reporting section on the website of the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). The IASB is a global organization that develops and promotes accounting standards and provides guidance on financial reporting.
Improving Return on Sales
Return on sales (ROS) is a critical metric that measures the amount of profit generated from each dollar of revenue earned. A high ROS indicates that a company is effectively managing its costs and generating significant profits. On the other hand, a low ROS suggests that a company may be struggling to control its expenses or facing other challenges.
To improve ROS, companies can adopt a range of cost management strategies and revenue enhancement tactics. The following subsections explore some of the most effective approaches.
Cost Management Strategies
One of the most straightforward ways to improve ROS is to reduce operational costs. This can be achieved by streamlining processes, reducing waste, and negotiating better deals with suppliers. For example, a company might invest in new technology to automate manual tasks, or renegotiate contracts with vendors to secure lower prices.
Another effective cost management strategy is to reduce overhead costs. This might involve downsizing the workforce, consolidating office space, or outsourcing certain functions to third-party providers. By reducing fixed costs, companies can improve their ROS and become more agile.
Revenue Enhancement Tactics
In addition to cost management strategies, companies can also focus on revenue enhancement tactics to improve their ROS. For example, they might invest in sales growth by expanding their product lines, entering new markets, or building stronger relationships with customers. Alternatively, they might focus on improving their sales activities by training sales reps, optimizing pricing strategies, or investing in marketing campaigns.
Another way to improve ROS is to reinvest profits back into the business. This might involve investing in new equipment, expanding production capacity, or launching new products. By reinvesting profits, companies can increase their operating expenses and generate more revenue in the long run.
To learn more about improving ROS, check out this resource from Investopedia.
Industry-Specific ROS Insights

When analyzing return on sales (ROS), it is important to take a closer look at specific industries to gain a more accurate understanding of how businesses within those industries are performing. Here are some insights into industry-specific ROS:
Service vs. Manufacturing Sectors
The service industry and manufacturing sector have different business models, which can greatly impact their ROS. Service-based businesses typically have higher labor costs and lower overhead costs, while manufacturing businesses have higher overhead costs and lower labor costs. As a result, service-based businesses tend to have lower ROS than manufacturing businesses.
According to industry statistics, the average ROS for the service industry is around 5-10%, while the average ROS for the manufacturing sector is around 10-15%. However, these numbers can vary greatly depending on the specific business and its competitors.
Cross-Industry ROS Comparisons
It can also be helpful to compare ROS across different industries to gain a better understanding of how a business is performing relative to its competitors. For example, a service-based business may compare its ROS to other businesses within the service industry, but it may also benefit from comparing its ROS to manufacturing businesses that have similar business models or target the same customer base.
One external resource that can provide valuable cross-industry ROS comparisons is the financial statements of publicly traded companies. By analyzing the financial statements of competitors within the same industry and across different industries, businesses can gain insights into how they stack up against their peers and identify areas for improvement.
Overall, understanding industry-specific ROS can provide valuable insights into a business’s financial performance and help identify areas for growth and improvement.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Fortune 500 Company Analysis
Return on Sales (ROS) is a crucial metric for any business, and it is especially important for large corporations. One Fortune 500 company that has consistently demonstrated strong ROS is Walmart. In 2023, Walmart reported annual sales figures of over $580 billion, with a ROS of 3.5%. This is a remarkable achievement, considering the size of the company and the intense competition in the retail industry.
Walmart’s success can be attributed to several factors, including its highly efficient supply chain, aggressive pricing strategy, and strong customer relationships. The company has also invested heavily in its sales team, providing extensive training and support to ensure that employees are equipped to provide exceptional service to customers.
Small Business ROS Strategies
Small businesses face unique challenges when it comes to achieving strong ROS. However, there are several strategies that can help these businesses succeed. One effective approach is to focus on building strong customer relationships. By providing exceptional service and personalized attention, small businesses can differentiate themselves from larger competitors and build a loyal customer base.
Another key strategy is to carefully manage expenses and optimize pricing. Small businesses may not have the same economies of scale as larger corporations, but they can still achieve strong ROS by keeping costs under control and pricing products and services appropriately.
One small business that has successfully implemented these strategies is a local bakery in downtown Seattle. By focusing on building strong relationships with customers and carefully managing expenses, the bakery has been able to achieve a ROS of 10% – significantly higher than the industry average.
In conclusion, Return on Sales is a critical metric for any business, regardless of size or industry. By studying successful companies like Walmart and implementing effective strategies like building strong customer relationships and managing expenses, businesses can achieve strong ROS and drive long-term success.
Here is a link to Investopedia’s detailed explanation of Return on Sales.
Future of Return on Sales

Emerging Trends and Predictions
Return on Sales (ROS) is an important metric that measures a company’s profitability. As companies continue to focus on increasing their profitability, there are several emerging trends and predictions that will shape the future of ROS.
One trend is the increasing importance of customer relationship management (CRM) systems. Companies are investing in CRM systems to better understand their customers and improve their sales channels. By using data analytics, companies can identify customer needs and tailor their products and services to meet those needs. This can lead to increased sales and higher ROS.
Another trend is the shift towards online sales channels. As more customers shop online, companies are shifting their focus to e-commerce. This requires companies to invest in technology and digital marketing to stay competitive. By leveraging technology, companies can improve their sales metrics and increase their ROS.
Technological Impact on ROS
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in shaping the future of ROS. One technology that is having a significant impact is artificial intelligence (AI). AI can analyze large amounts of data and provide insights that can help companies improve their sales channels and increase their ROS.
Another technology that is having an impact is blockchain. Blockchain technology can improve supply chain management and reduce costs, which can lead to higher ROS. By using blockchain, companies can create a more transparent and efficient supply chain, which can improve customer satisfaction and increase sales.
In conclusion, the future of ROS is shaped by emerging trends and technological advancements. Companies that invest in technology and focus on improving their sales channels and CRM systems will be better positioned to increase their ROS. As the business landscape continues to evolve, it’s important for companies to stay ahead of the curve and adapt to new trends and technologies.
Here is a link to Investopedia that provides more information on Return on Sales.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is the return on sales ratio calculated?
The return on sales ratio, also known as the net profit margin, is calculated by dividing the net income by the total revenue. The resulting percentage indicates how much of each dollar of revenue is kept as profit after all expenses have been paid.
What constitutes a strong return on sales percentage?
A strong return on sales percentage varies by industry, but generally, a higher percentage indicates better profitability. According to Investopedia, a return on sales percentage of 10% or higher is considered good for most businesses.
How can return on sales be improved?
Return on sales can be improved by increasing revenue or decreasing expenses. This can be achieved through various strategies such as increasing prices, reducing costs, and improving operational efficiency.
What is the difference between return on sales and return on investment (ROI)?
Return on sales measures the profitability of a company by comparing the net income to the total revenue, while return on investment measures the efficiency of an investment by comparing the net profit to the total investment. Return on sales is a measure of profitability, while return on investment is a measure of efficiency.
Can return on sales be used to assess a company’s profitability?
Yes, return on sales is a commonly used metric to assess a company’s profitability. It provides insight into how much profit a company is generating from its revenue.
How does return on sales compare to return on capital (ROC)?
Return on capital (ROC) measures the return on all capital invested in a company, including debt and equity, while return on sales only measures the return on revenue. ROC takes into account the amount of capital invested in a company, while return on sales does not.